Published 2019-07-12.
Last modified 2024-08-10.
Time to read: 2 minutes.
This lecture discusses how to work with arrays in Scala, and discusses related types provided by Scala.
The sample code for this lecture can be found in
courseNotes/.
Array
scala.Array
is pretty much what you might expect: an ordered collection of items of similar type, accessible via an index.
Scala arrays are implemented as a thin wrapper around
java.util.Array, which means that they are mutable.
Arrays are also the most performant collection type for many operations.
It is easy to create a Scala Array; in the following example the type of the Array
elements is detected by the Scala compiler as Int.
scala> val a1 = Array(1, 2, 3) a1: Array[Int] = Array(1, 2, 3)
The REPL shows us that a1 has type Array[Int].
This is the syntax to create an empty Array of type Int:
scala> val a2 = Array.empty[Int] a2: Array[Int] = Array()
You can explicitly declare the type of an Array variable.
scala> val a3: Array[Int] = Array(1, 2, 3) a3: Array[Int] = Array(1, 2, 3)
You can modify an Array.
For example, we can increment the first element of an array this way:
scala> a1(0) = a1(0) + 1 a1 res0: Array[Int] = Array(2, 2, 3)
The Scala compiler desugars this expression:
a1(0) = a1(0) + 1
...into:
a1.update(0, a1.apply(0) + 1)
The update
method changes an element of a Scala array.
Predefined Implicit Conversions
Scala provides predefined implicit conversions to enrich arrays with extra capabilities.
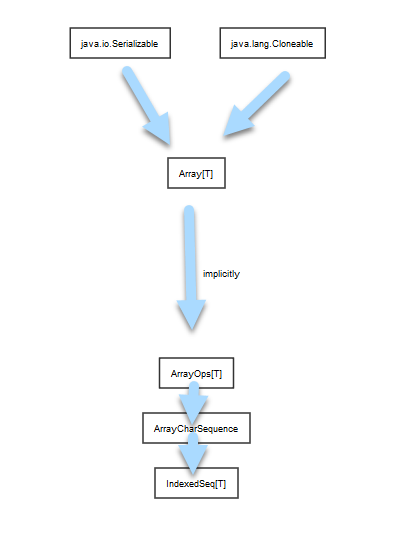
The Array Scaladoc Type Hierarchy diagram shows that the
ArrayOps
implicit class enriches Array;
it also shows that Scala predefines an implicit converter from Array to Java’s
CharSequence.
Because Scala 2.13 damaged the generation of type hierarchy diagrams, I’ve added some blue arrows to show relationships;
some are due to object-oriented inheritance and some are due to implicit conversion.
You can convert an Array to another Scala collection type by using the appropriate conversion method,
such as toList, toSeq, toBuffer, etc.
We will learn about these Scala collection types over the next several lectures.
An entire lecture is dedicated to
To Converters.
© Copyright 1994-2024 Michael Slinn. All rights reserved.
If you would like to request to use this copyright-protected work in any manner,
please send an email.
This website was made using Jekyll and Mike Slinn’s Jekyll Plugins.
